Q4 2025 Crypto Report: Asset Performance and Sector Highlights

Bitcoin
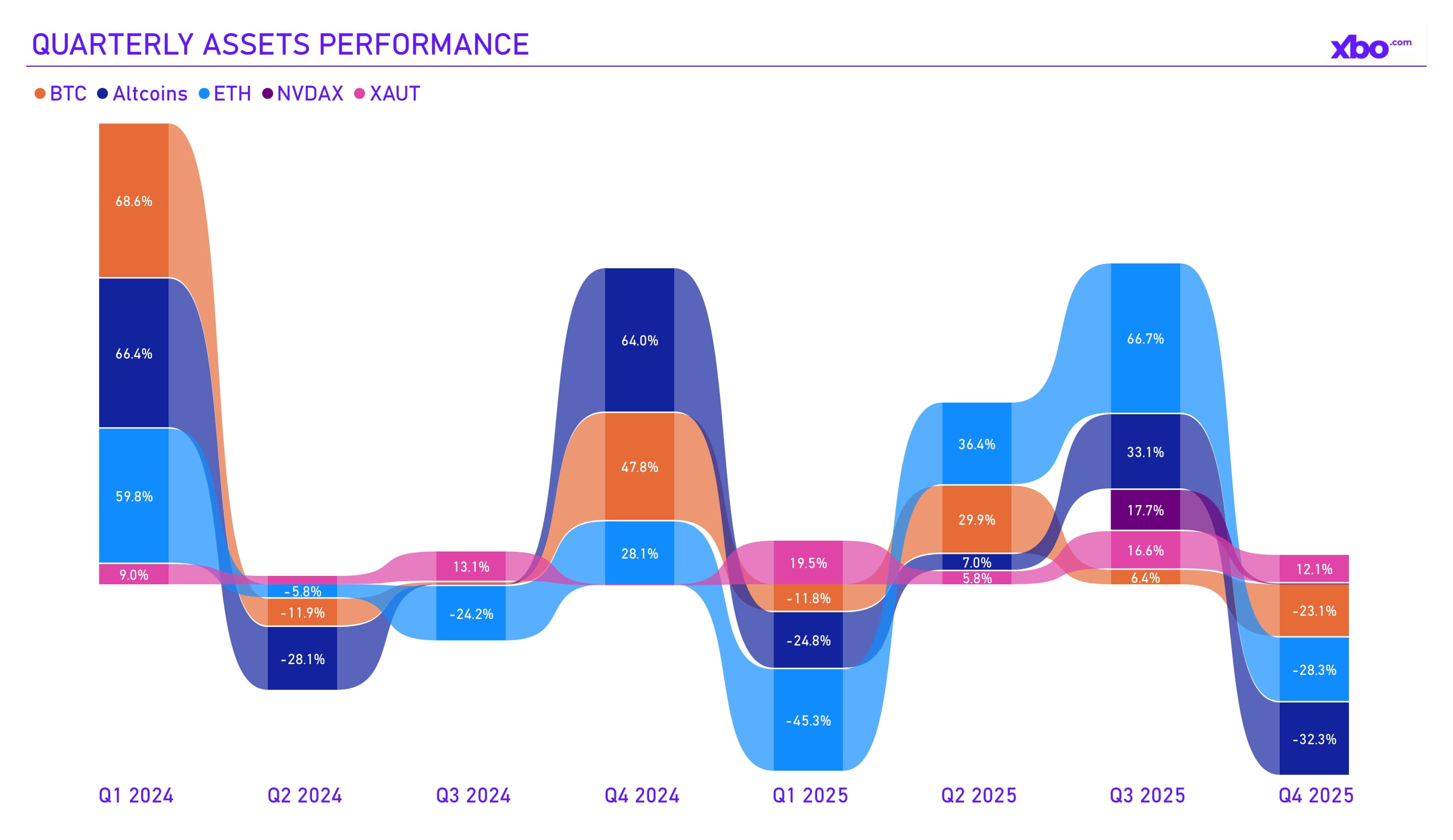
Source: xbo.com, tradingview.com
The last quarter of 2025 ended in the negative territory, with a number of external factors causing this: US tariff policy, Trump's confrontation with Fed Chair Jerome Powell, strengthening of the Japanese yen and carry-trade liquidations, gaps in macroeconomic data due to the prolonged US government shutdown, and more. Among the observed assets at the end of the quarter, tokenized gold proved to be the most profitable, tokenized Nvidia stocks finished in second place, and the altcoin sector as a whole showed the weakest performance.
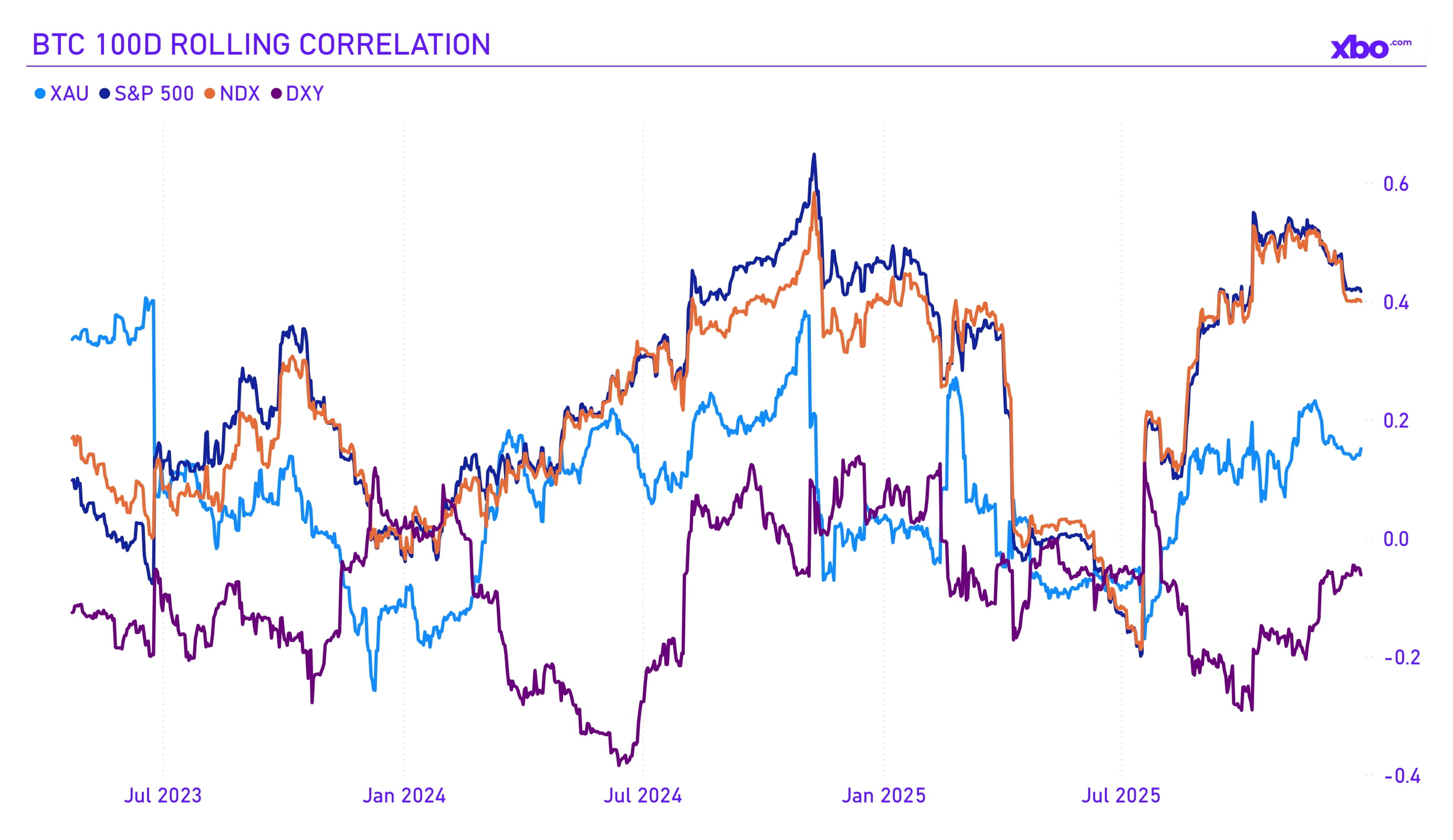
Source: CoinMarketCap, investing.com
Bitcoin's correlation with stock market indices remained relatively high throughout the fourth quarter; however, BTC underperformed. Its correlation with gold remained in the neutral zone. As observed, gold rose actively amid economic and political uncertainty in the US and globally, while Bitcoin reacted more painfully to the news. The dollar index is traditionally inversely correlated with Bitcoin, but at the moment there is no clear contrary reaction from Bitcoin to DXY movements; a broader risk-off sentiment in Bitcoin contributed to this behavior.
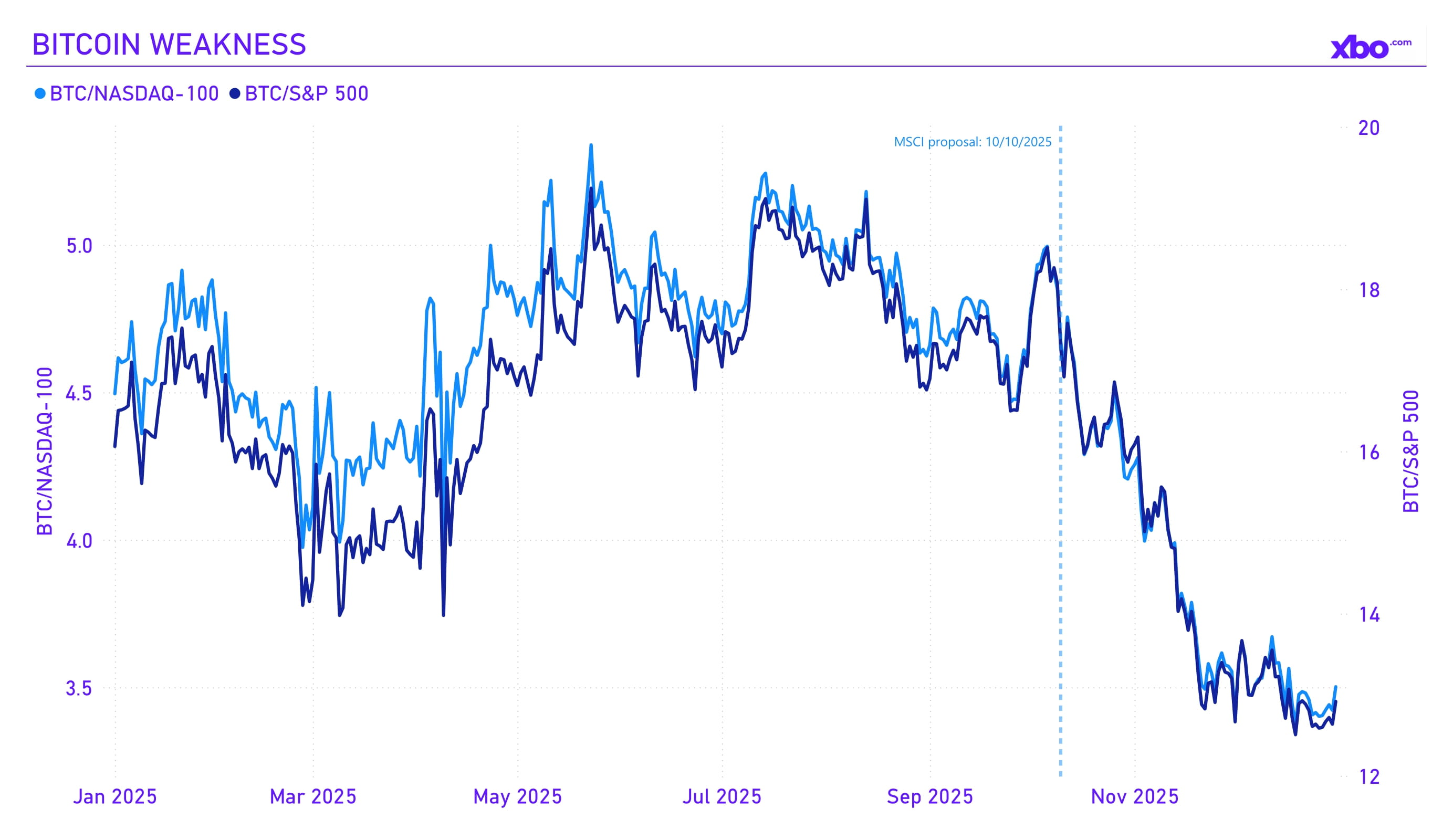
Source: nasdaq.com, investing.com
Bitcoin's weakness during the fourth quarter has already been mentioned twice – but what caused it? Analysts emphasize that on October 10, MSCI put forward a proposal to exclude companies with more than 50% crypto assets on their balance sheets from its indices. This was a subtle yet extremely important development, and from that moment Bitcoin began to weaken relative to the stock indices with which it correlates. This move poses a direct threat to Bitcoin treasuries such as Strategy, since the exclusion from indices would force passive funds (such as Vanguard, pension funds, and ETFs tracking stock indices) to sell Strategy shares and similar equities. JPMorgan estimated the potential outflow from Strategy alone at $2.8 billion.
Despite the fact that insolvency does not threaten Strategy, there is still a risk of Bitcoin sales on its side if the MSTR share price decreases significantly. This could trigger a chain reaction: as the share price falls, the share premium would decrease, leading to the drop in the ratio of share capitalization to net asset value (NAV), and making new liquidity for Saylor's strategy more expensive. And if traders start receiving margin calls due to a decline in shares, the amount of Bitcoin sales could increase even further. At the moment, however, this risk has passed, as DAT companies remained in the indices.
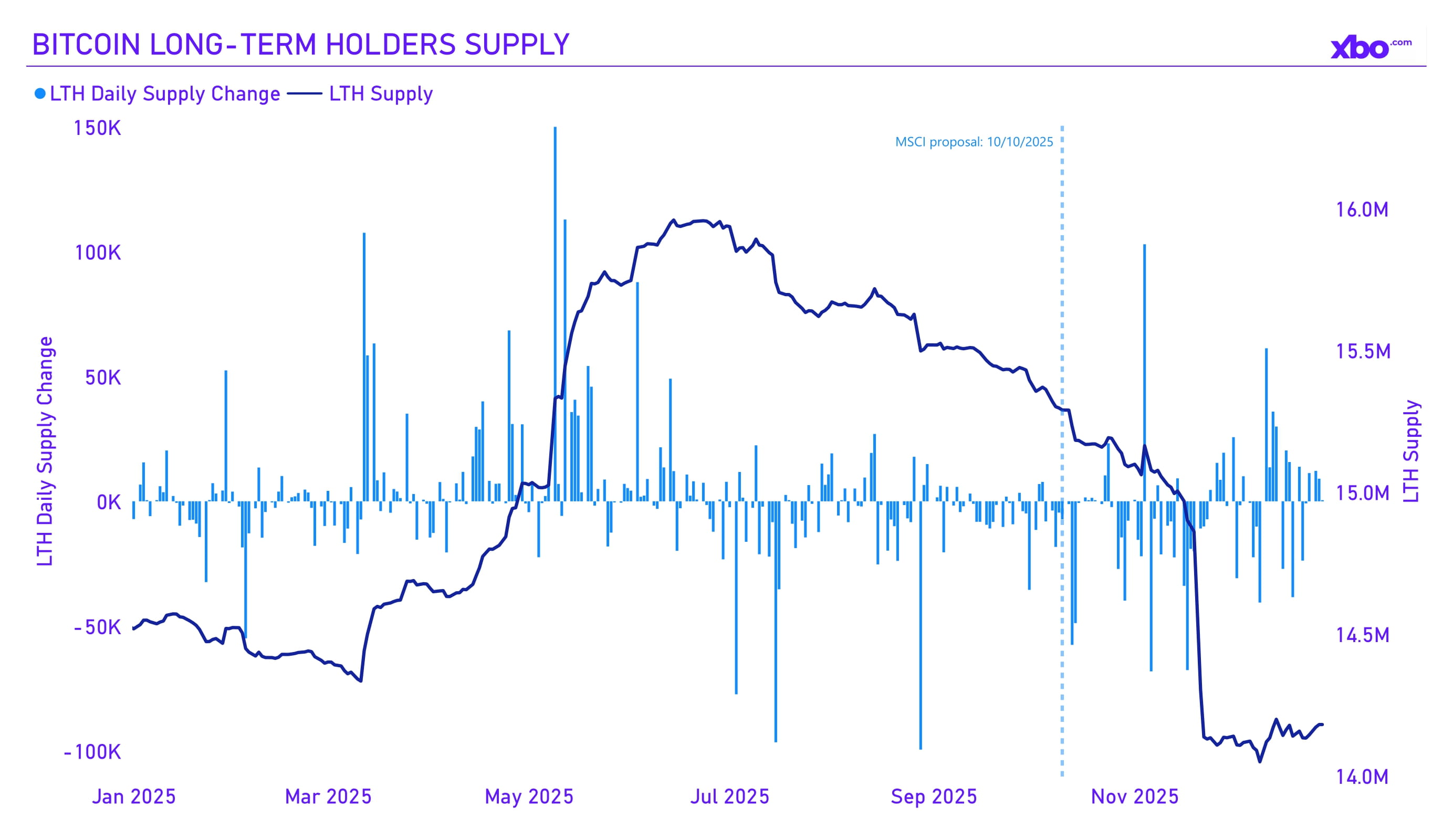
Source: bgeometrics.com
Long-term holders continued to reduce their Bitcoin positions; however, after the publication of the MSCI proposal, sales became both more active and larger. This suggests that either such holders are “splitting” their balances into smaller, less noticeable wallets in order to avoid panic during large sales, or that they do not believe Bitcoin will return to its historical highs in the medium term. Closer to the end of the year, however, sales have noticeably declined.
Source: bgeometrics.com
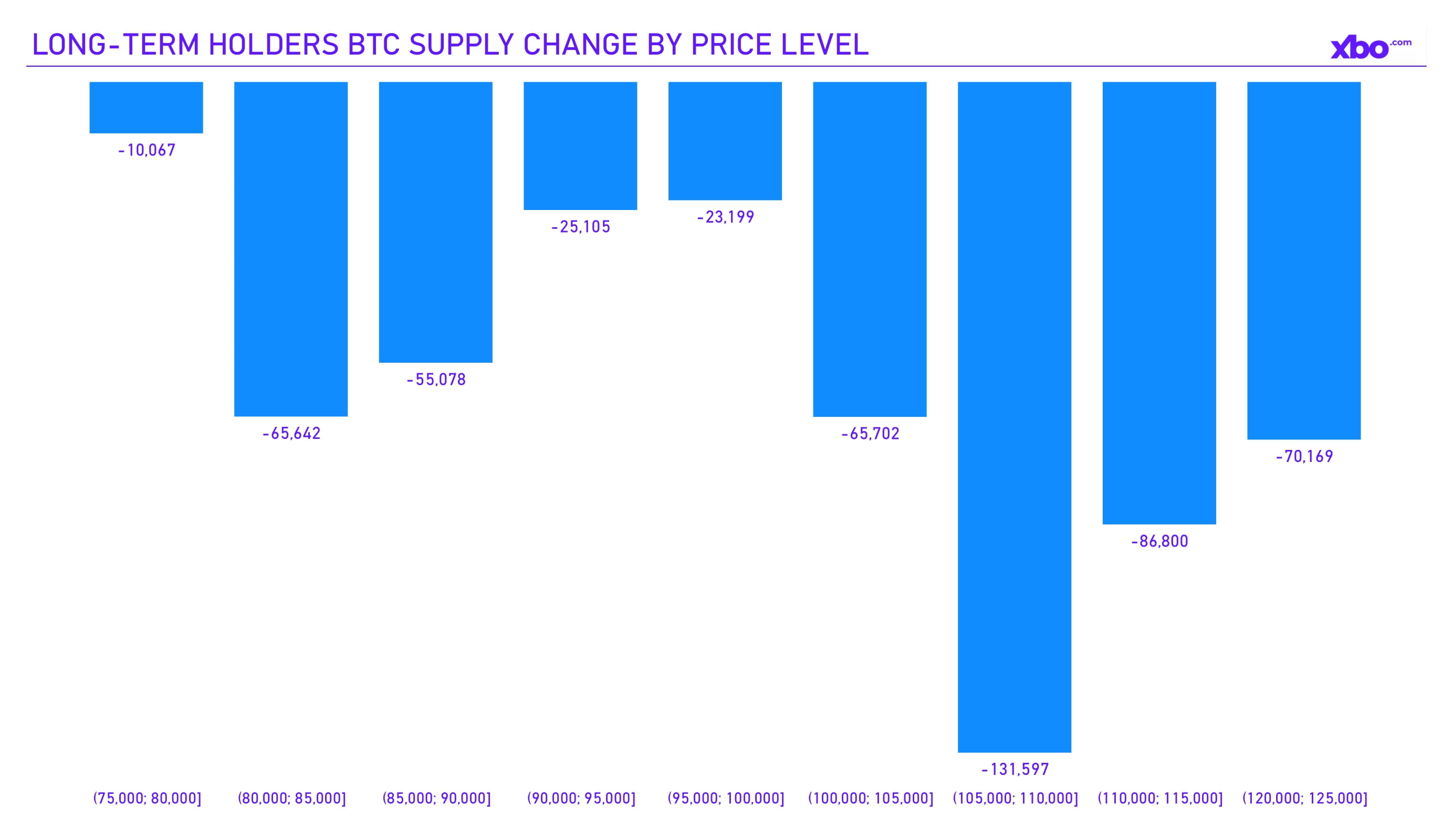
In terms of price ranges, long-term holders did not accumulate positions in any range during the current quarter. Notably, sales volumes increased precisely within ranges corresponding to key levels: quarterly highs and lows, as well as resistance levels. At the same time, activity decreased in intermediate ranges. This indicates that holders tried to neutralize the impact of their sales by executing them in zones with higher liquidity. This supports the view that holders were actively selling their BTC rather than redistributing them across their own addresses.
Source: bgeometrics.com
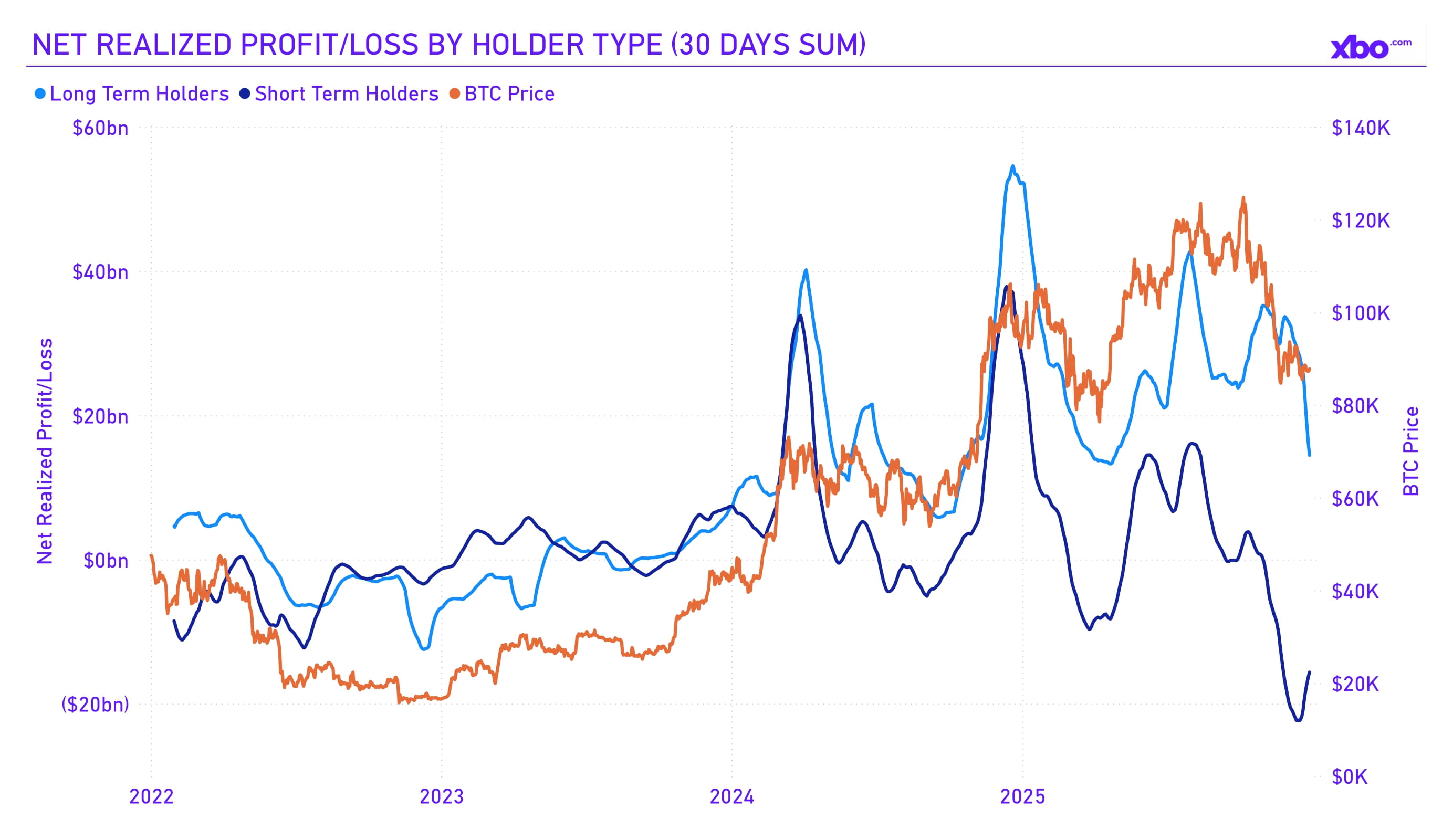
The market was significantly unsettled by risks associated with BTC DATs. Additionally, the number of loss-making positions increased. Further declines in Bitcoin were driven by mass capitulation among traders and short-term holders. On December 13, the floating loss of short-term holders over a one-hundred-day horizon exceeded $22 billion, setting an absolute anti-record. Long-term holders, on the contrary, realized profits totaling $14 billion by the end of the year due to a lower cost basis.
Despite generally positive analyst expectations for 2026, Bitcoin is no longer viewed as the primary market favorite and, according to experts, is likely to lag behind its "younger siblings”. Moreover, in Q4, only about half of the Bitcoin volume traded in Q3 was realized – 470 thousand BTC versus 989 thousand BTC, respectively. This creates a risk of further decline, as there remains supply available for capitulation. In addition, amid mass adoption and tokenization, investors are increasingly interested in infrastructure projects capable of generating stable revenue, while the potential upside of most promising assets is considered higher than of Bitcoin.
Ethereum
By the results of the fourth quarter of 2025, ETH had fallen by 23%, showing weaker dynamics than Bitcoin. Why, then, do experts consider ETH more attractive? The answer lies in Ethereum's infrastructural potential. While Bitcoin is positioned as “digital gold”, Ethereum is more functional, and under current conditions of tokenization and the potential convergence of stock market liquidity with the crypto market, ETH has strong chances to outperform Bitcoin in terms of growth rates.
In this context, a key event for the Ethereum ecosystem in the fourth quarter was the Fusaka upgrade launched on December 3. Its main focus was data scaling for L2. Key changes introduced by the upgrade included a reduction in node load and an eightfold expansion of blob capacity, as well as an increase in the gas limit to support a higher number of transactions on L1. Overall, the upgrade was aimed at reducing commission costs and improving the blockchain's performance.
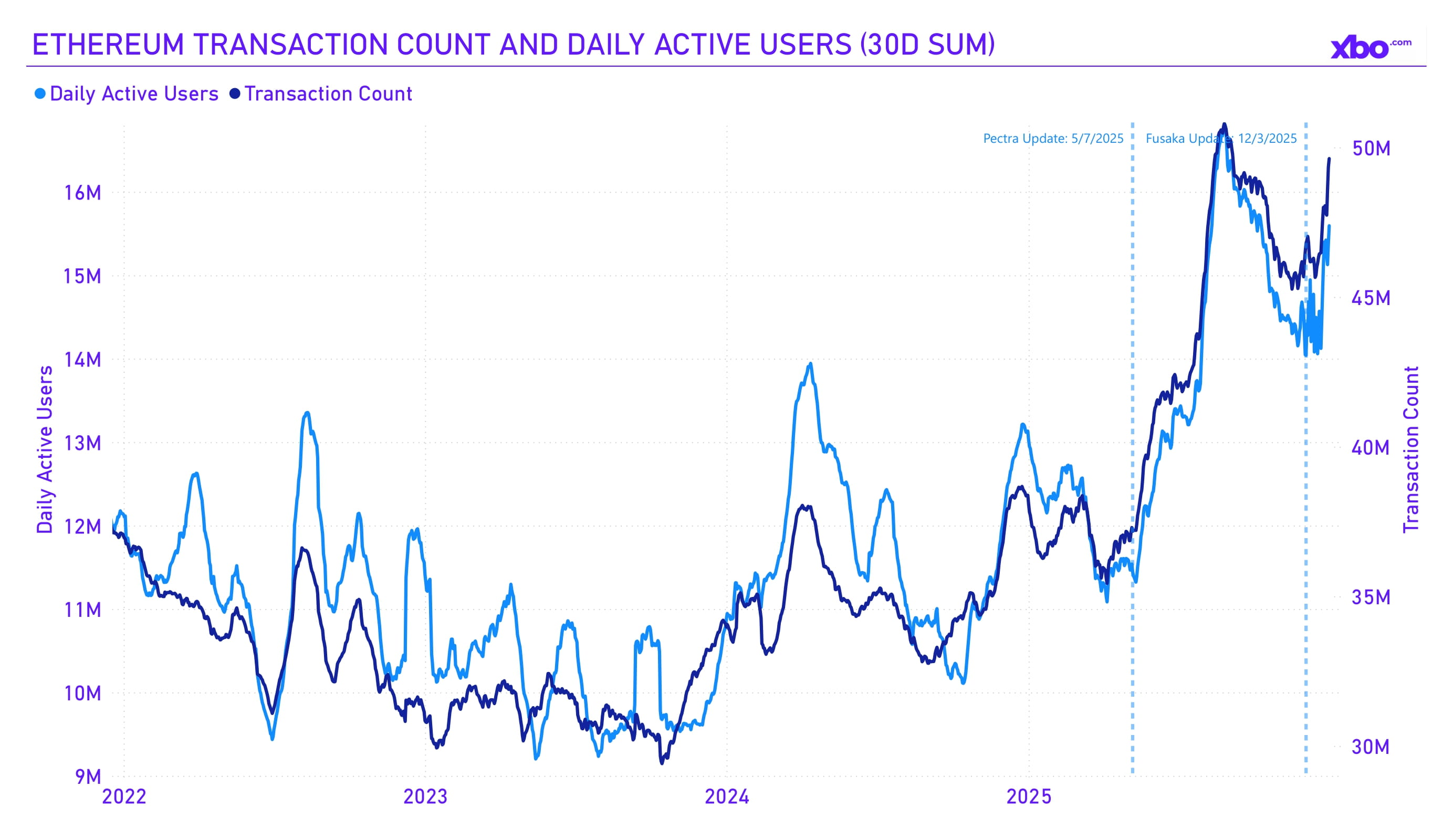
Source: artemisanalytics.com
After the Pectra upgrade, the number of transactions and users on the network began to grow at accelerated rates. This is a positive development for the ecosystem, as increased network activity raises the rate of ETH burning. From a pricing perspective, it is critical that burning remains balanced with issuance or exceeds it; otherwise, ETH supply dilution could lead to inflation. Under the current upgrade strategy of the development team, lower fees are expected to be offset by higher user activity. A similar effect is therefore anticipated from the Fusaka upgrade.
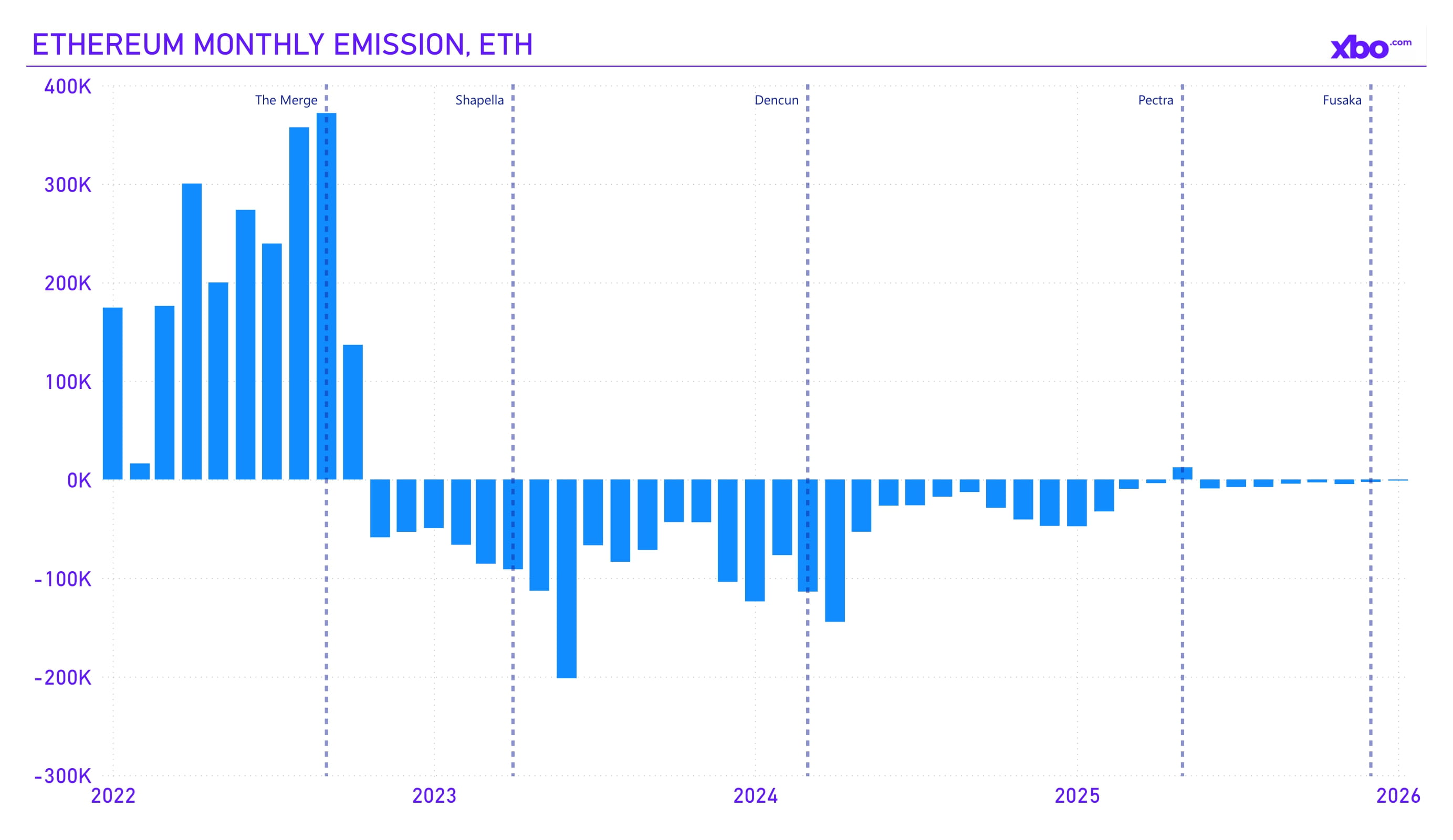
Source: etherscan.io
The impact of the upgrades was clearly reflected in the overall ETH supply: following the Pectra upgrade, burning volumes began to exceed ETH issuance.
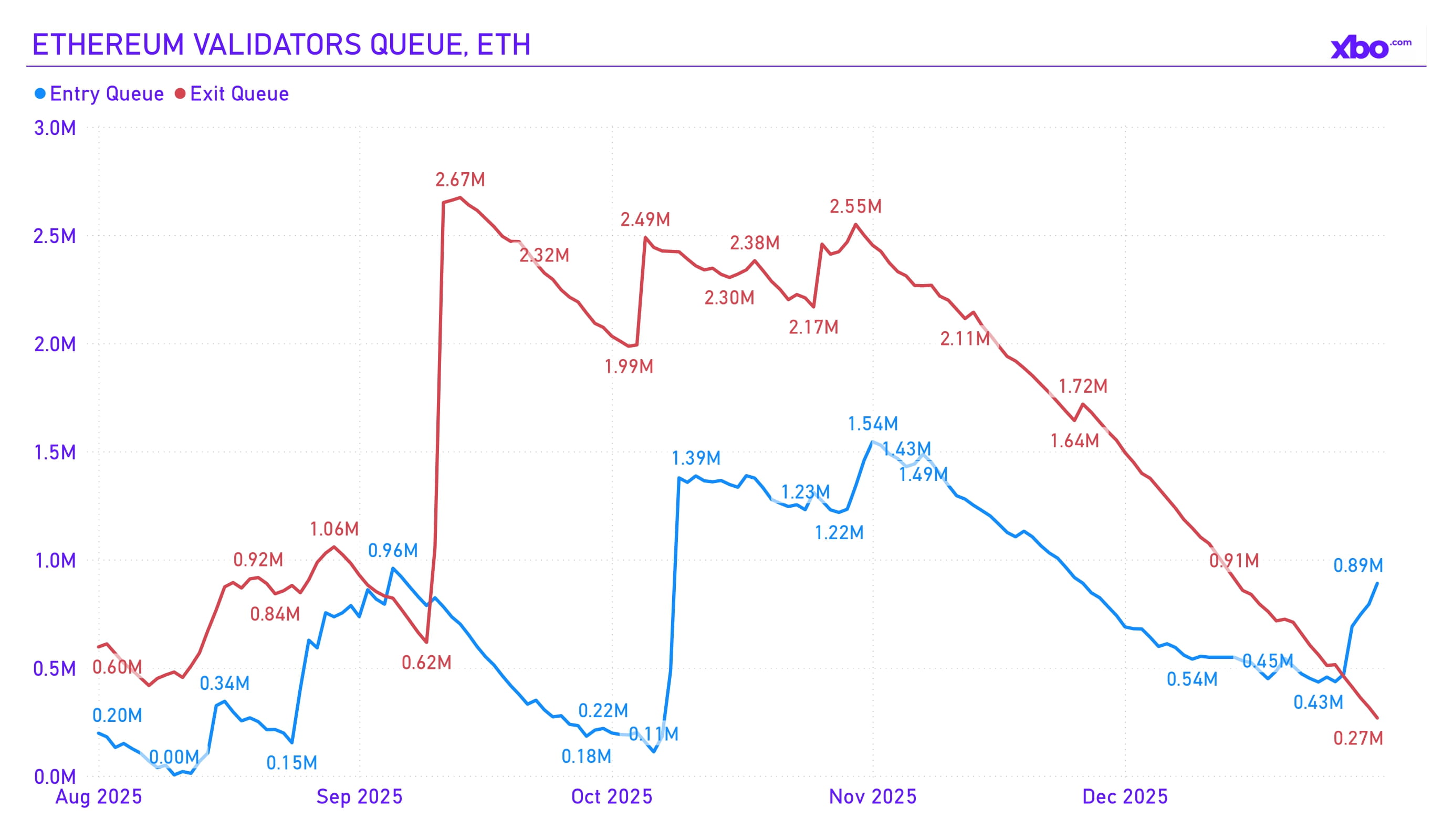
Source: dune.com
In the fourth quarter, a sharp increase was observed in the queue for withdrawing ETH from native staking; however, the entry queue grew as well, albeit with a delay. Initially, this was perceived as a threat of mass selling; however, for the most part, this dynamic turned out to merely be a rotation of ETH between validators. This pattern persisted until the end of the year, and at the moment the staking entry queue once again exceeds the withdrawal queue.
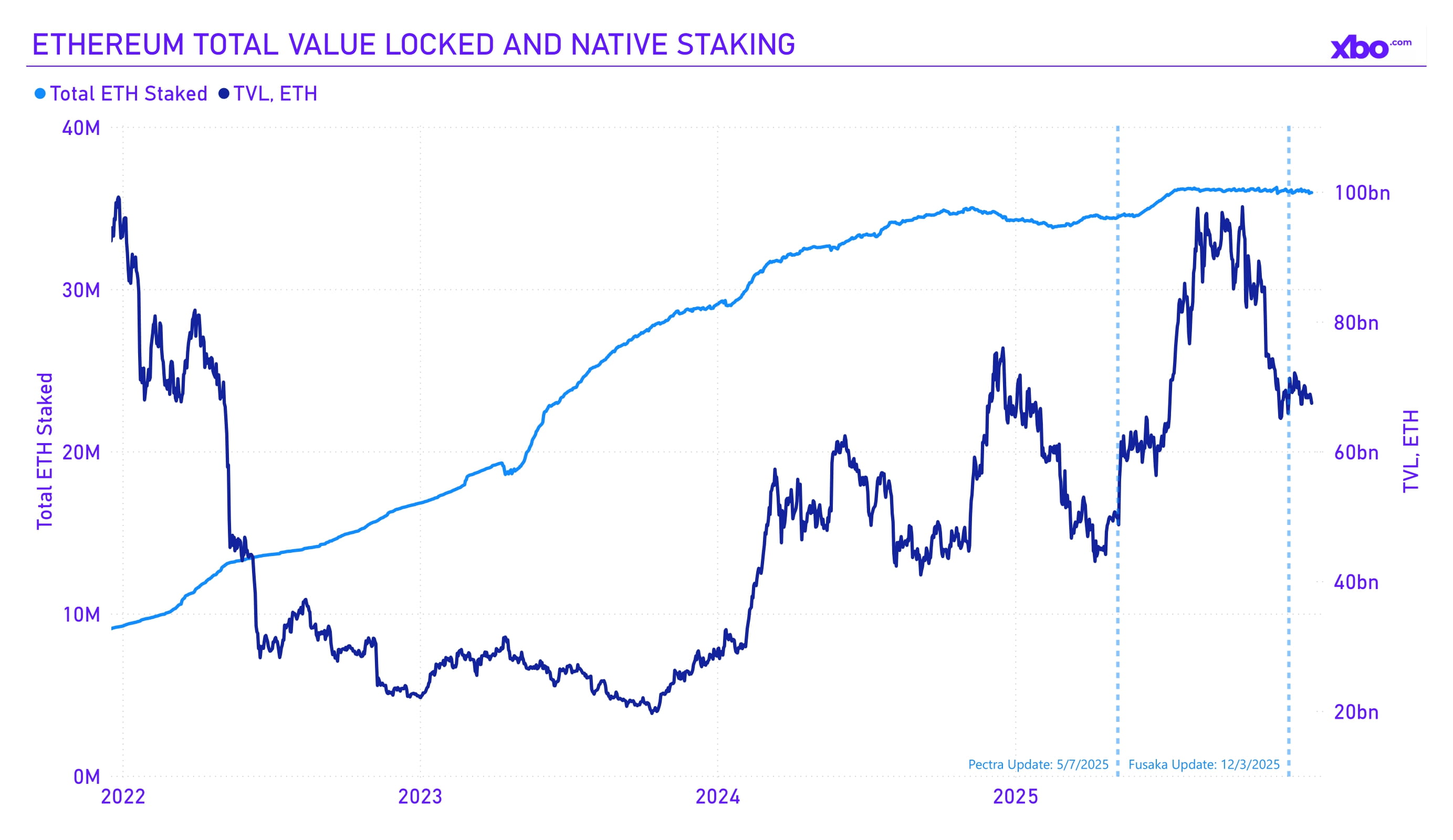
Source: artemisanalytics.com
Pectra lowered the staking threshold, so the amount of ETH in staking began to grow; however, Ethereum still went through correction, reducing its monetary valuation. In addition, even with the increase in the ETH staking withdrawal queue, the total amount of staked ETH in native terms remained stable.
Despite the price correction, infrastructural improvements and the deflationary mechanism strengthen Ethereum's long-term position as a leading platform for tokenization, DeFi, and integration with traditional finance, creating a foundation for it to potentially outperform Bitcoin.
Crypto ETFs and Corporate Crypto Purchases
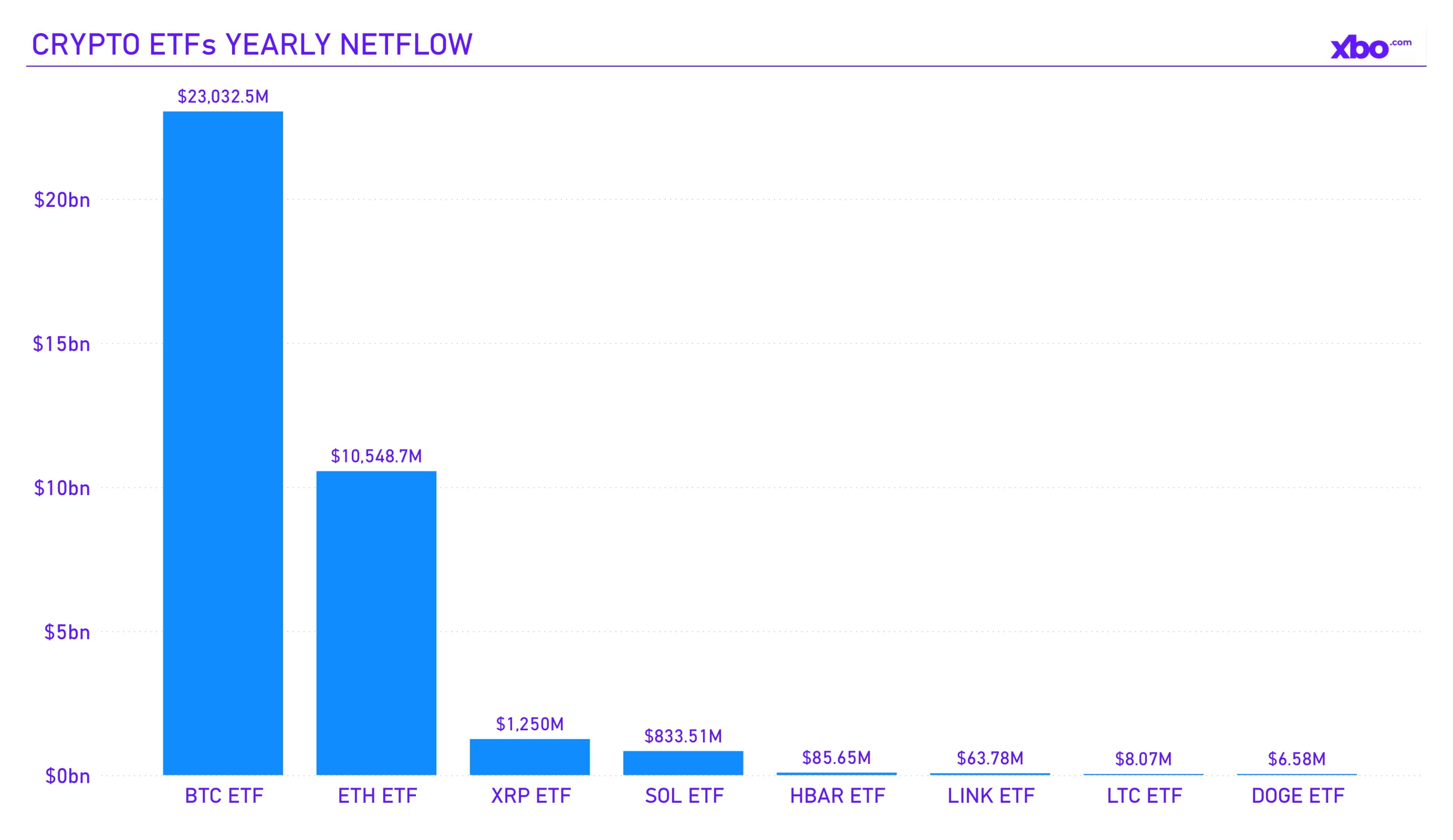
Source: sosovalue.com
In the fourth quarter of 2025, the crypto ETF sector, tokenized treasuries, and corporate crypto acquisitions held on balance sheets showed mixed dynamics amid the broader crypto market correction. Total inflows for the year reached $23 billion into BTC ETFs and $10.5 billion into ETH ETFs. New altcoin ETFs also emerged, although their aggregate inflows over the year remained relatively insignificant.
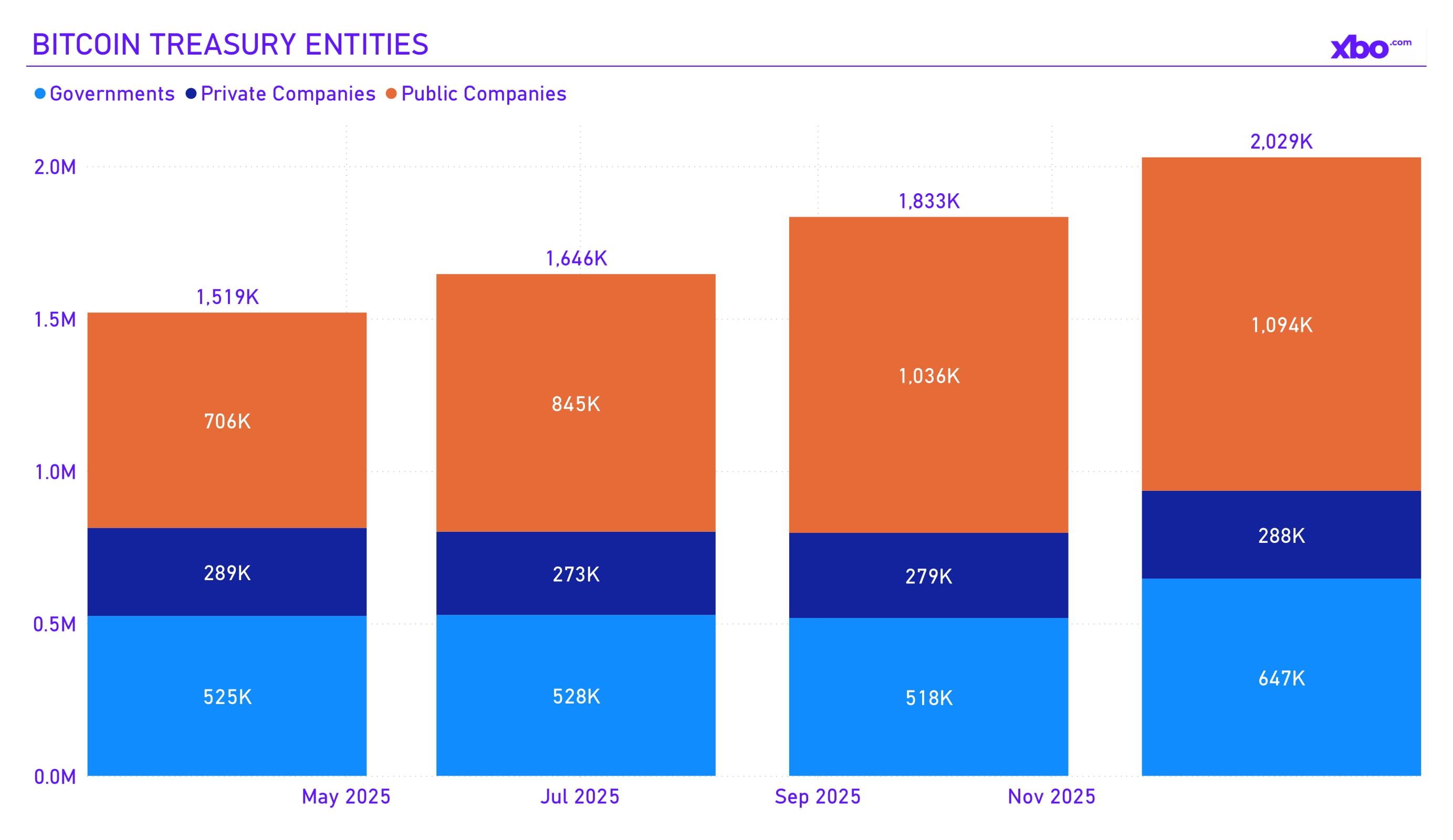
Source: bitcointreasuries.net
Corporate Bitcoin purchases slowed down: only nine new companies joined the trend compared to 53 in Q3, although major players such as MicroStrategy continued accumulation. The total volume of corporate BTC holdings increased by approximately 195,000 BTC during the quarter. However, 65% of corporate treasuries ended the period with unrealized losses due to the price correction.
The market correction, driven by macroeconomic factors such as Fed tightening and geopolitical tensions, led to an outflow of retail capital. Meanwhile, it simultaneously stimulated institutional buying on dips, reinforcing the long-term narrative of crypto as a hedge against inflation and debt.
Regulatory clarity also contributed to market development: settlements with Ripple and Coinbase, along with new legislation, reduced risks and supported dip-buying activity. At the same time, elevated volatility resulted in loss-making treasuries, slowing the pace of new entries.
On the other hand, crypto ETFs and tokenized treasuries strengthened the role of the US dollar by increasing demand for Treasuries as reserves, supporting the financing of the $38.4 trillion national debt through indirect institutional demand. On a global scale, they improved cross-border payments and asset tokenization, potentially adding $1–2 trillion in efficiency to global trade by reducing transaction costs. Corporate crypto purchases diversified balance sheets and hedged inflation risks; however, they also introduced systemic threats: in the event of a crisis, these structures could trigger shocks similar to those seen in the banking sector, affecting monetary stability.
These trends furthered the institutionalization of crypto: ETFs, to some extent, mitigated the Q4 correction by attracting hedge fund inflows. Tokenized treasuries and corporate holdings enhanced DeFi and RWA liquidity but increased correlation with traditional assets. Balance sheet purchases, such as those by MicroStrategy, created proxy exposure for investors, while unlocks and corrections contributed to increased altcoin volatility.
Banks also adapted to the changing environment by integrating crypto-related products. Wells Fargo accepted BTC ETFs as collateral for loans, while Bank of America introduced ETF-related consultations for clients. Tokenized treasuries began competing with traditional deposits, potentially attracting $1–2 trillion according to some estimates, prompting institutional players like BlackRock or Fidelity to invest in digitization in order to reduce fees and provide 24/7 access.
As a result, the fourth quarter of 2025 became a period of consolidation between the TradFi sector and crypto through crypto ETFs, tokenized treasuries, and corporate purchases, with record inflows and accumulation observed despite the market correction. Regulatory maturity and institutional demand laid the groundwork for growth in 2026, enhancing economic efficiency and hedging capabilities, while simultaneously increasing systemic risks. This highlights crypto’s transition from speculation to deeper integration with traditional finance, which requires a delicate balance between the benefits of innovation and the associated risks.
US Macroeconomics
For the US economy, the last quarter of 2025 was characterized by sustained growth, despite ongoing challenges in the form of inflationary pressure and rising government debt. According to the Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta's GDPNow model estimates, real GDP grew by 5.1% annualized, significantly exceeding the Q3 figure of 4.3%. This momentum was driven by strong consumer demand, technology investments, and a recovery in the services sector, although it coincided with a slowdown in the labor market. Overall, annual GDP growth for 2025 is estimated at 1.9–2.6%. These trends have direct implications for the crypto sector, where volatility intensified due to correlation with risk assets and monetary expectations.
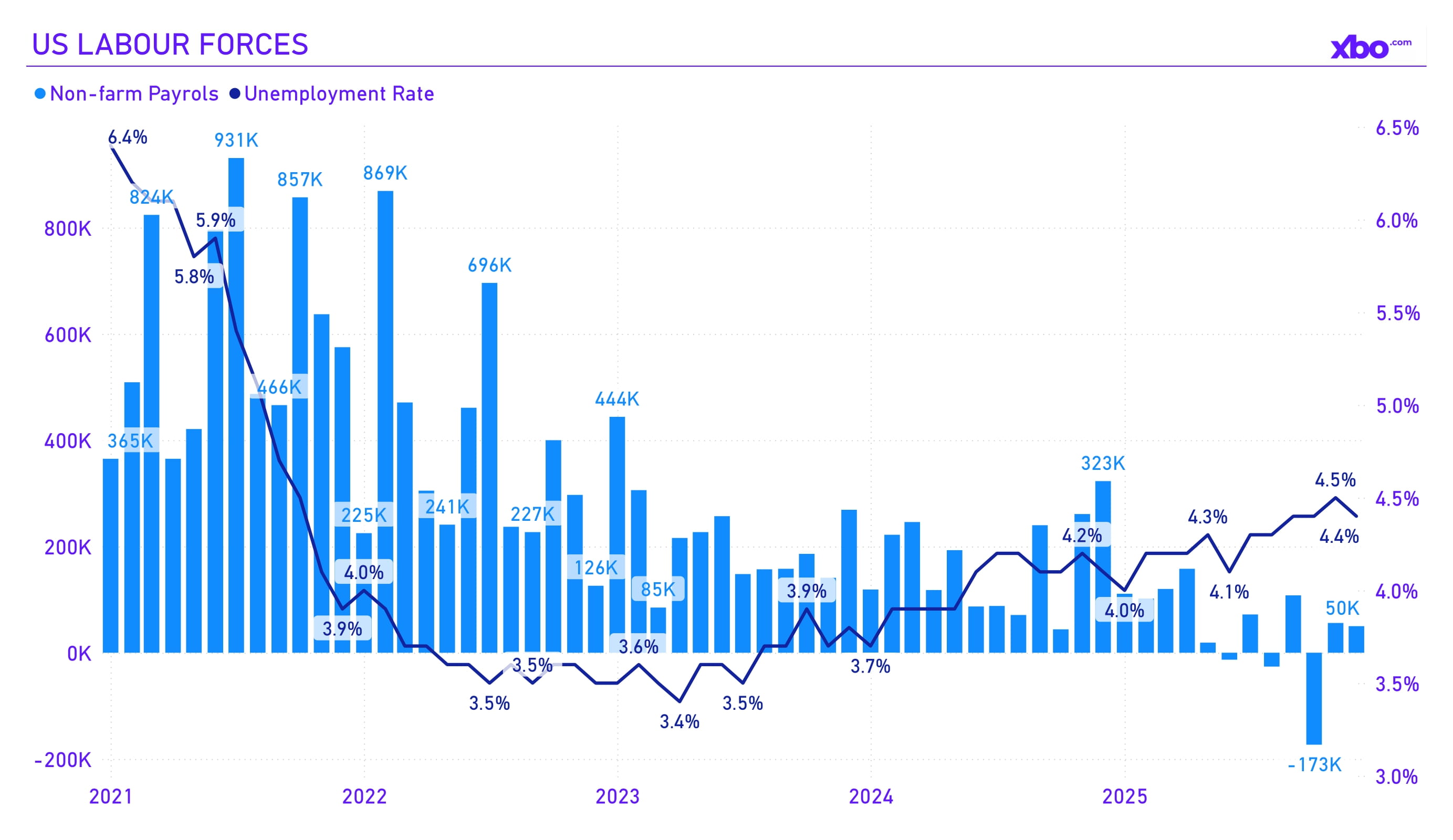
Source: fred.stlouisfed.org
The unemployment rate for 2025 rose to 4.4%, indicating relative stability. However, the pace of job creation slowed, with only 50,000 positions added in December. The average annual unemployment rate was around 4.2–4.5%, with CBO forecasts projecting growth to 4.6% in 2026.
The slowdown in hiring is linked to monetary policy tightening in previous quarters, which increased borrowing costs for businesses and reduced investment activity. At the same time, low unemployment supports consumer spending, contributing to inflationary pressure. For the crypto sector, this is a dual factor: a stable labor market strengthens retail interest in digital assets as an alternative to traditional investments, while slowing employment growth may signal risks, provoking capital outflows from volatile markets, as observed in Q4 with the decline in crypto market capitalization.
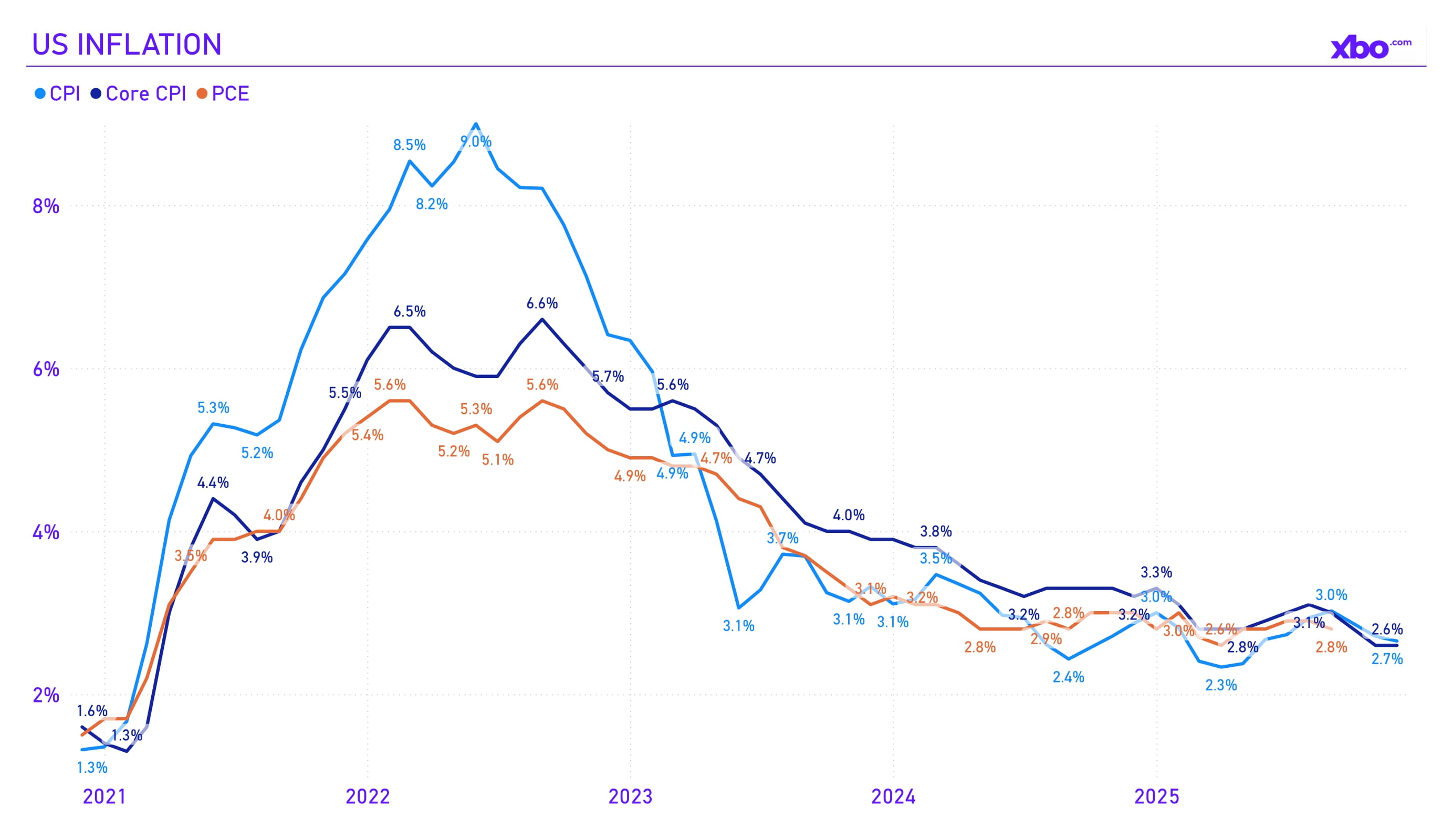
Source: bls.gov, fred.stlouisfed.org
Inflation remained elevated but showed signs of stabilization. The CPI index in December rose by 0.3% m/m, with an annual rate of 2.7%, while PCE reached 2.8% in September. Core PCE inflation was projected at 2.6–2.7% by year-end, which is above the Fed’s target level of 2%.
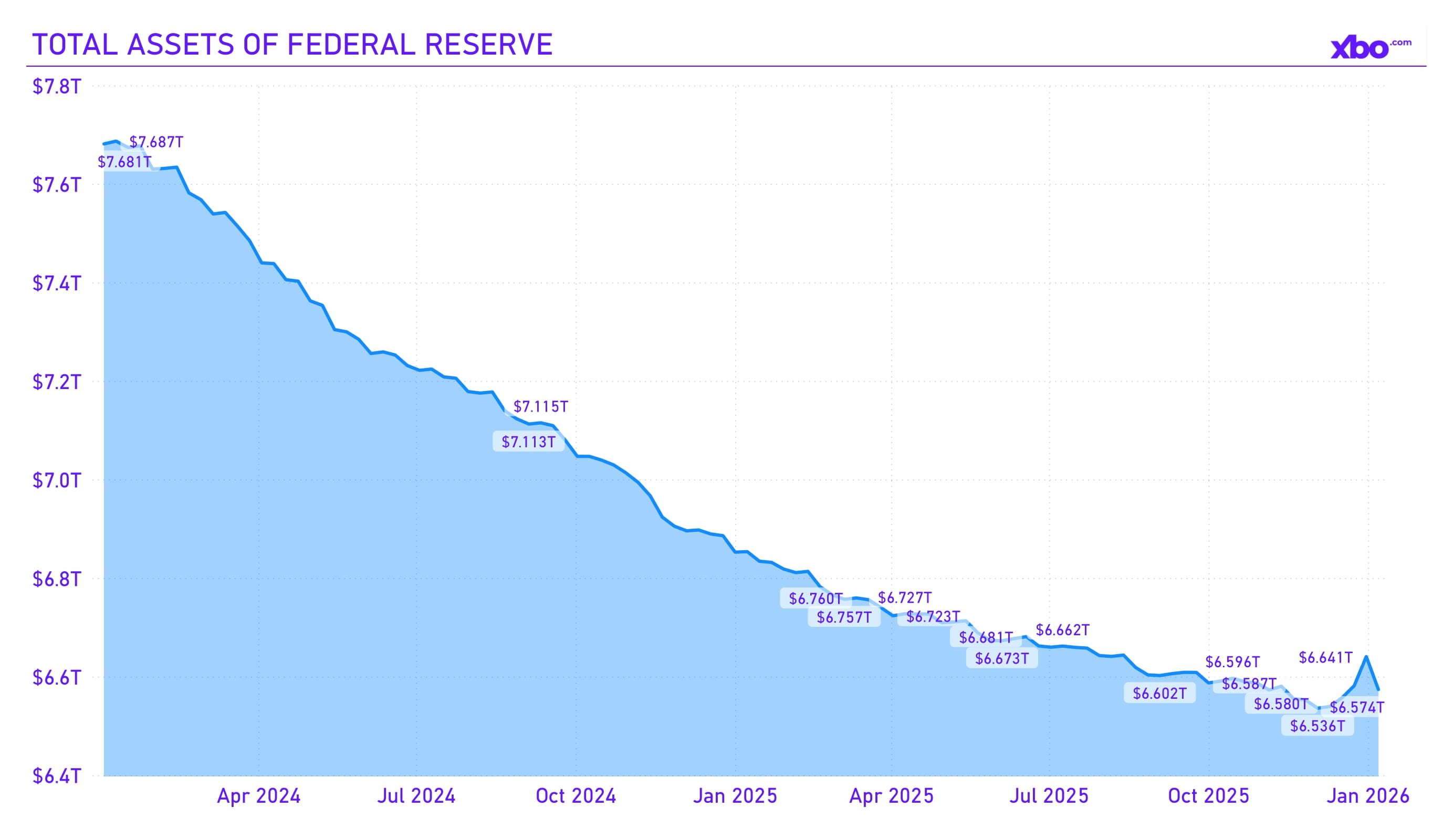
Source: federalreserve.gov
For this reason, the Fed continued its course of cautious easing: at the December meeting, rates were cut by 0.25 percentage points to 3.75%, marking the third cut in 2025 after a pause in the first half of the year. The Committee highlighted economic uncertainty, with emphasis on the balance between employment and inflation. By the end of December, the Fed’s balance sheet slightly increased to the level of $6.64 trillion, following the cessation of balance sheet reduction on December 1 and the beginning of expansion from December 12 to stabilize short-term rates.
The rate cut was implemented as a response to slowing hiring and recession risks. However, it was constrained by inflation, giving statements a “hawkish” tone. Balance sheet expansion increased liquidity, stimulating lending and investment, while also raising concerns about long-term inflation. For crypto, this is a positive development, as lower rates reduce the attractiveness of bonds and redirect capital into risk assets. In Q4, the crypto market showed a mixed reaction – institutional inflows grew, but we overall capitalization declined.
The US national debt reached $38.40 trillion by December, increasing by $2.23 trillion over the year. The budget deficit for fiscal year 2025 amounted to $1.8 trillion, which is 2% lower than the previous year, but still exceeding $1 trillion annually. Debt-to-GDP exceeded 124%, intensifying pressure on fiscal sustainability.
For these reasons, US macroeconomics in Q4 2025 had a mixed impact on crypto: strong GDP growth and rate easing stimulated institutional interest, with additional positive sentiment coming from regulatory changes. However, inflation and uncertainty in Fed policy triggered a correction. In the long-term narrative, BTC’s deflationary mechanics and DeFi position crypto as a hedge against inflation and debt, while short-term risks amplify volatility. Expectations for 2026 suggest crypto may outperform traditional assets if easing continues, but fiscal risks require close monitoring.
Stablecoins
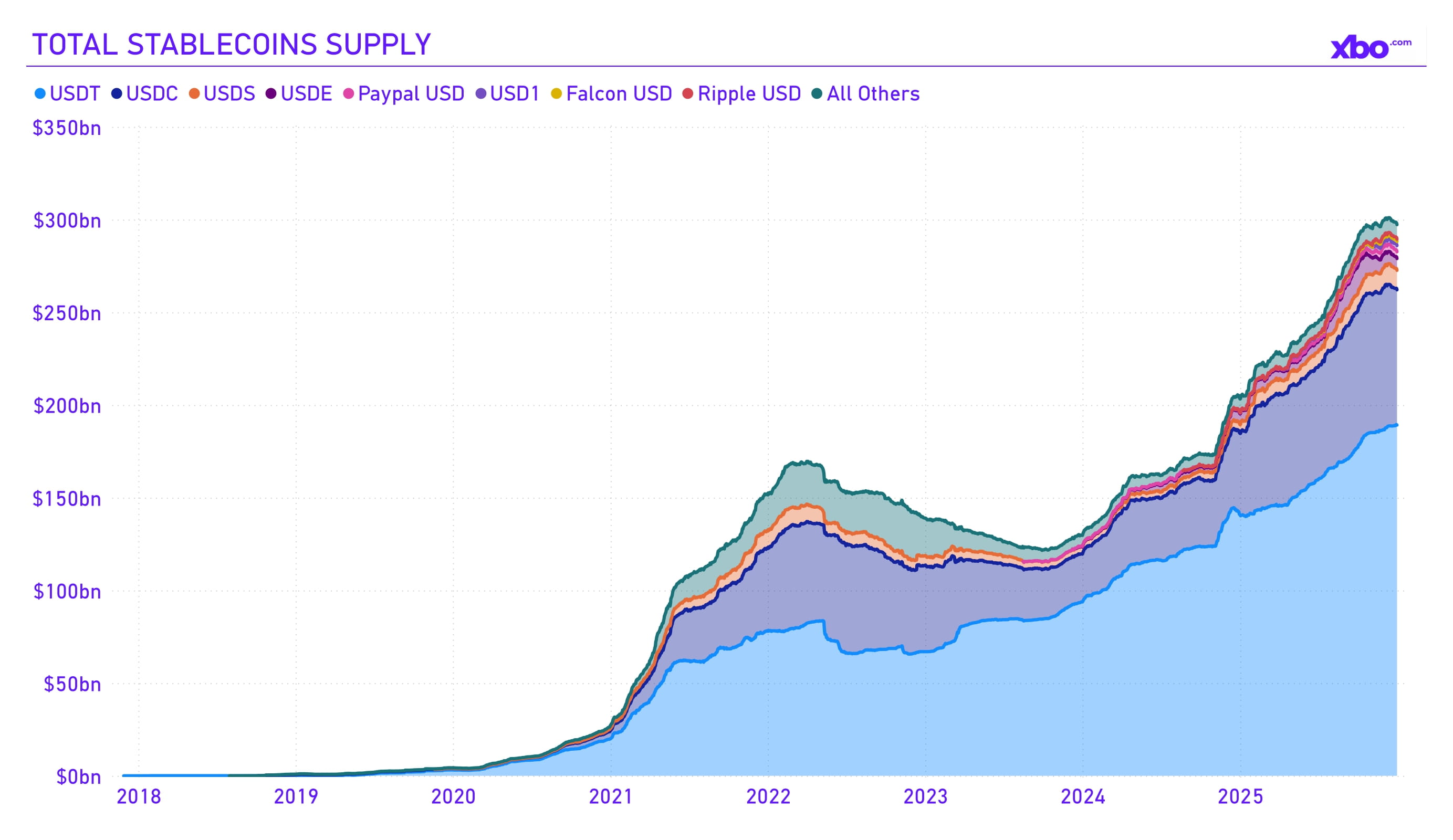
Source: app.rwa.xyz
In the fourth quarter of 2025, the stablecoin sector continued to demonstrate record growth, confirming its role as a key element of the crypto ecosystem and global finance. The total capitalization of stablecoins increased from approximately $288 billion in Q3 to $297 billion by the end of the year. According to RWA.xyz data, transaction volume reached a historical high of over $19 trillion for the quarter, contributing to a 2025 total of $57 trillion. This momentum was driven by institutional interest, infrastructure improvements, and favorable regulatory changes, such as the adoption of the GENIUS Act in the United States, which introduced frameworks for the issuance and supervision of stablecoins. Market leaders such as USDT and USDC dominated, with most of their circulating supply growth occurring on the Ethereum network.
Stablecoins strengthen the global role of the US dollar, since most of them are pegged to USD, increasing demand for American Treasuries as reserve assets. In the US, this supports fiscal stability and helps to finance the growing national debt through indirect demand for bonds, while also creating dependence on crypto markets. Globally, stablecoins improve cross-border payments by reducing transaction costs and settlement time, which is especially beneficial to emerging economies. Overall, they accelerate asset tokenization and the convergence of traditional and digital finance, potentially improving global trade efficiency in the long term.
Stablecoins also compete with bank deposits, and some estimates suggest they could displace $1–2 trillion in credit by 2030 due to lower fees and 24/7 availability. Banks are adapting by integrating stablecoins into their services, which changes the structure of balance sheets and increases their efficiency. For institutions, this tendency opens new opportunities in DeFi; however, it also creates risks of deposit outflows and the need for new regulatory models. Competition from stablecoins forces banks to invest in digitization, which accelerates innovation but may potentially reduce the profitability of traditional banking, prompting sector consolidation.
Thus, the Q4 2025 strengthened the position of stablecoins as a transformational instrument, with record growth and regulatory maturity. Their influence enhances the efficiency of financial systems in the US and globally by enabling improved payments – yet it still carries financial stability risks. In crypto, they stimulate growth, while for banks, they drive evolution, emphasizing the need to balance innovation with regulation for sustainable development.
Altcoins and Key DeFi Sectors
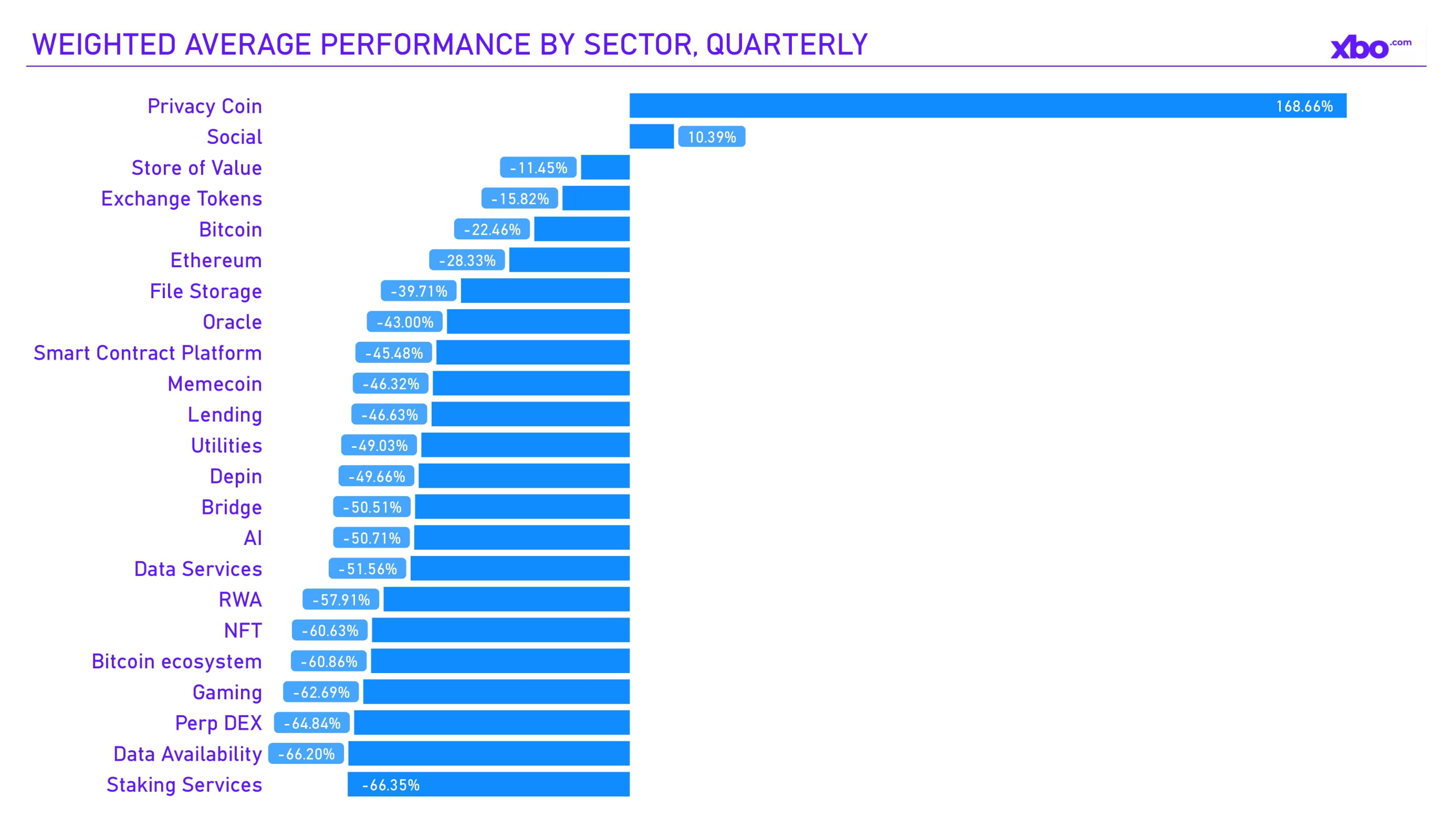
Source: artemisanalytics.com
In the final quarter of 2025, the altcoin market significantly underperformed amid overall crypto volatility, with total altcoin capitalization decreasing from approximately $800 billion to $541 billion by year-end, as per TradingView. Privacy-focused altcoins were a rare positive exception, with ZEC leading in growth amid increased regulatory attention to data privacy, driven by topics such as fully homomorphic encryption (FHE) and confidential transactions. Other sectors, including memecoins and AI-related tokens, showed mixed results, with speculative pumps in tokens like PUMP and TAO. Still, sector-weighted returns remained negative.
This weakness was caused by Bitcoin's sustained dominance (reaching 58–59%), institutional inflows into BTC and ETH ETFs, and the dilution effects from new token launches. As a result, the market split: institutional altcoins such as LINK or HYPE stabilized due to enterprise integrations, while speculative projects showed a 97% failure rate over months.
Therefore, the decline in aggregate TVL of the crypto sector was expected; however, while TVL fell in dollar terms, it actually increased in native tokens for the top blockchains
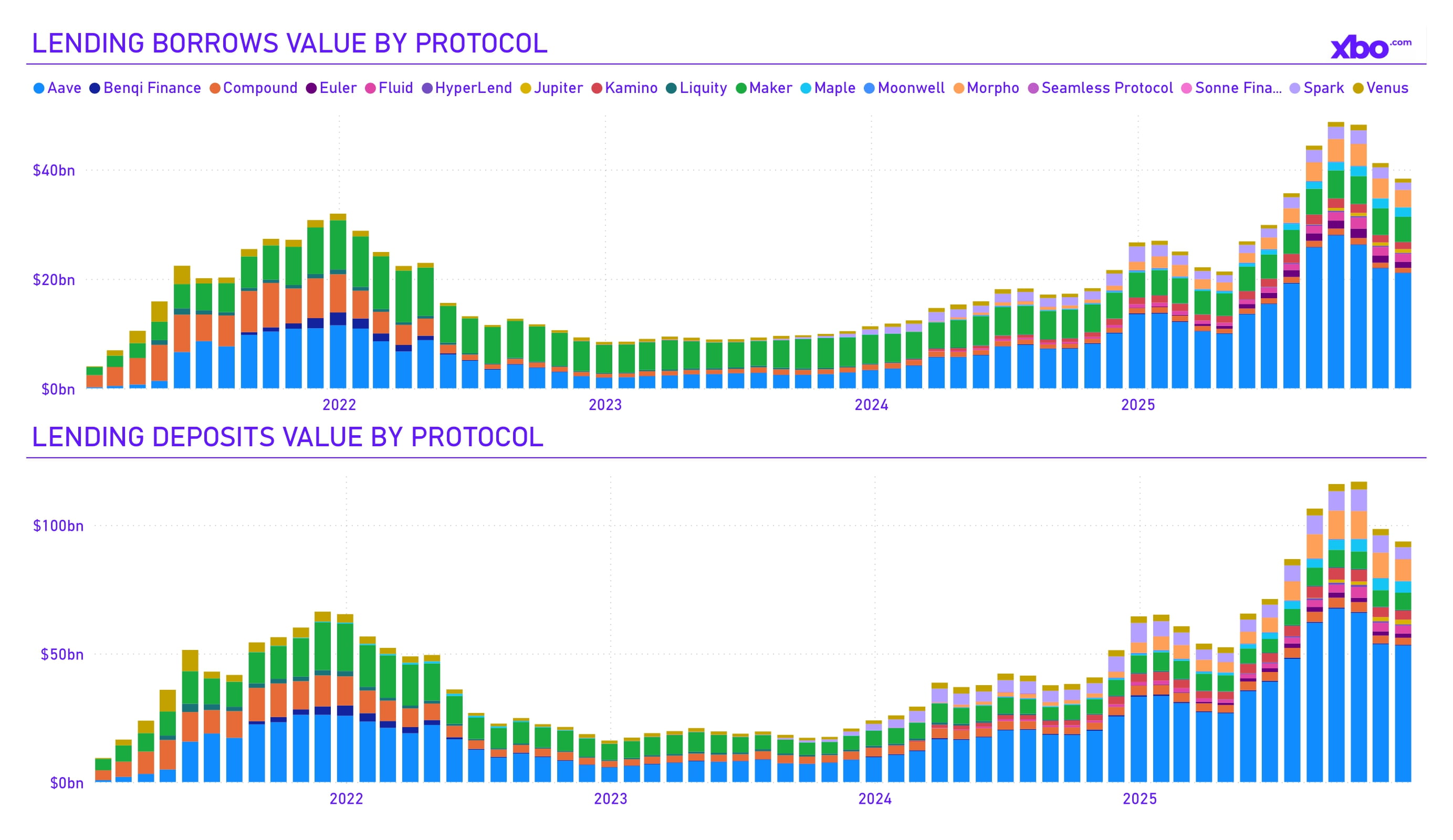
Source: artemisanalytics.com
In the Lending sector, deposit and loan capitalization declined slightly. Still, the overall power alignment remained unchanged, with AAVE in first place, for which total deposits and loans at year-end amounted to $53 billion and $21 billion respectively.
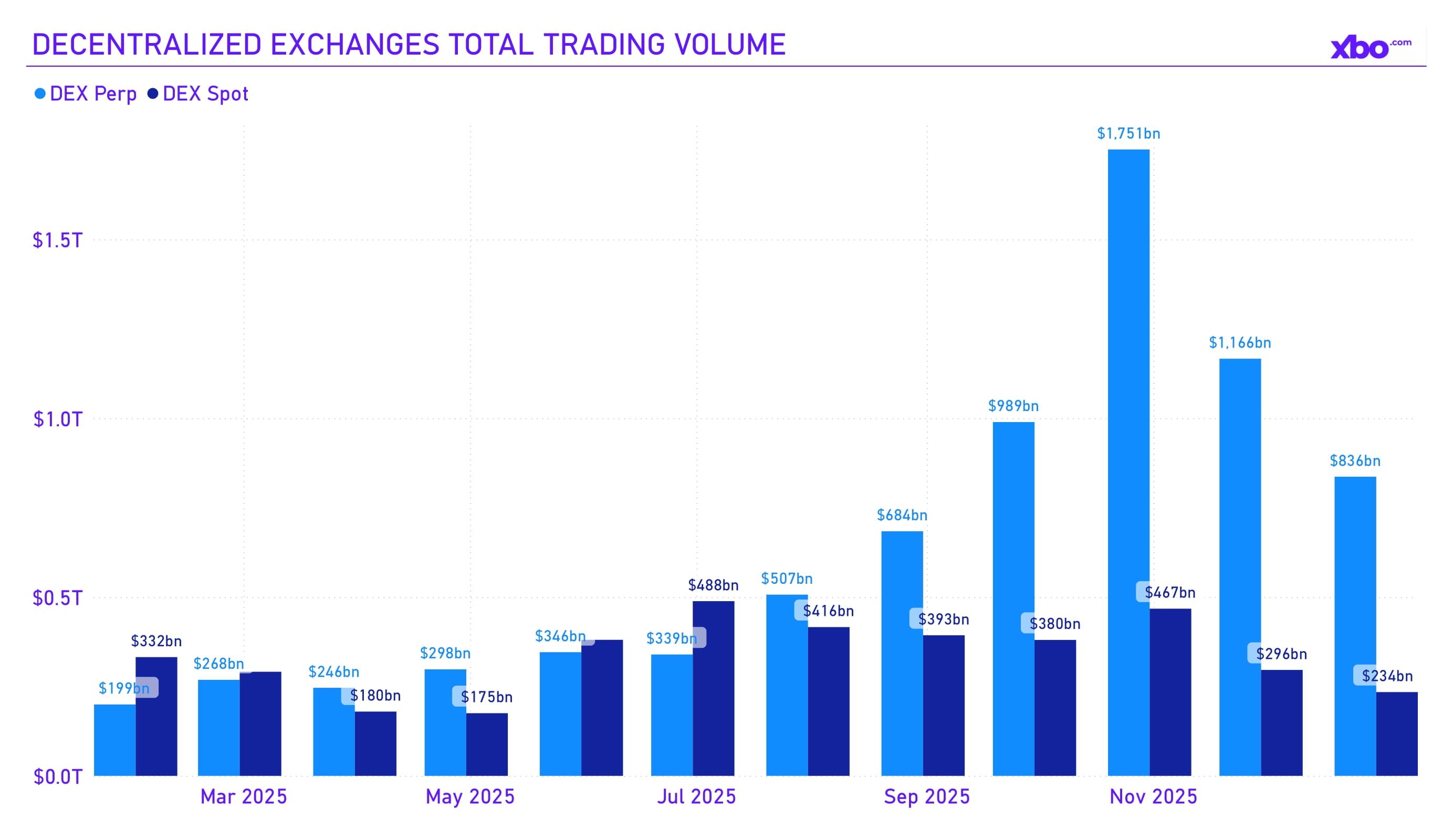
Source: artemisanalytics.com
DEX trading volumes increased overall for the quarter, supported by November data, although activity still showed signs of decline.
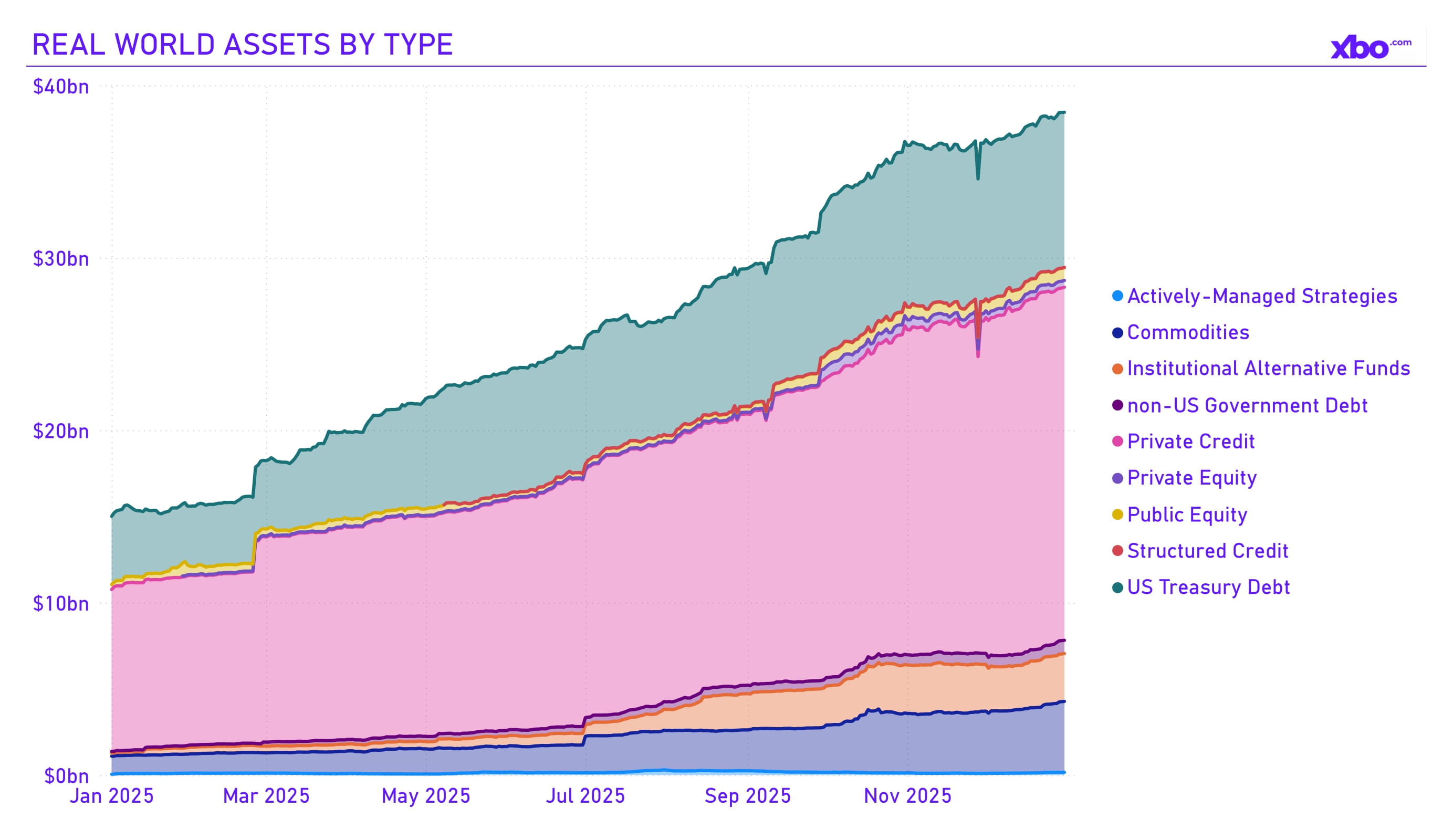
Source: app.rwa.xyz
The volume of tokenized assets increased by $5.7 billion in the fourth quarter. Currently, the capitalization of RWA assets excluding REPO operations stands at $39.6 billion.
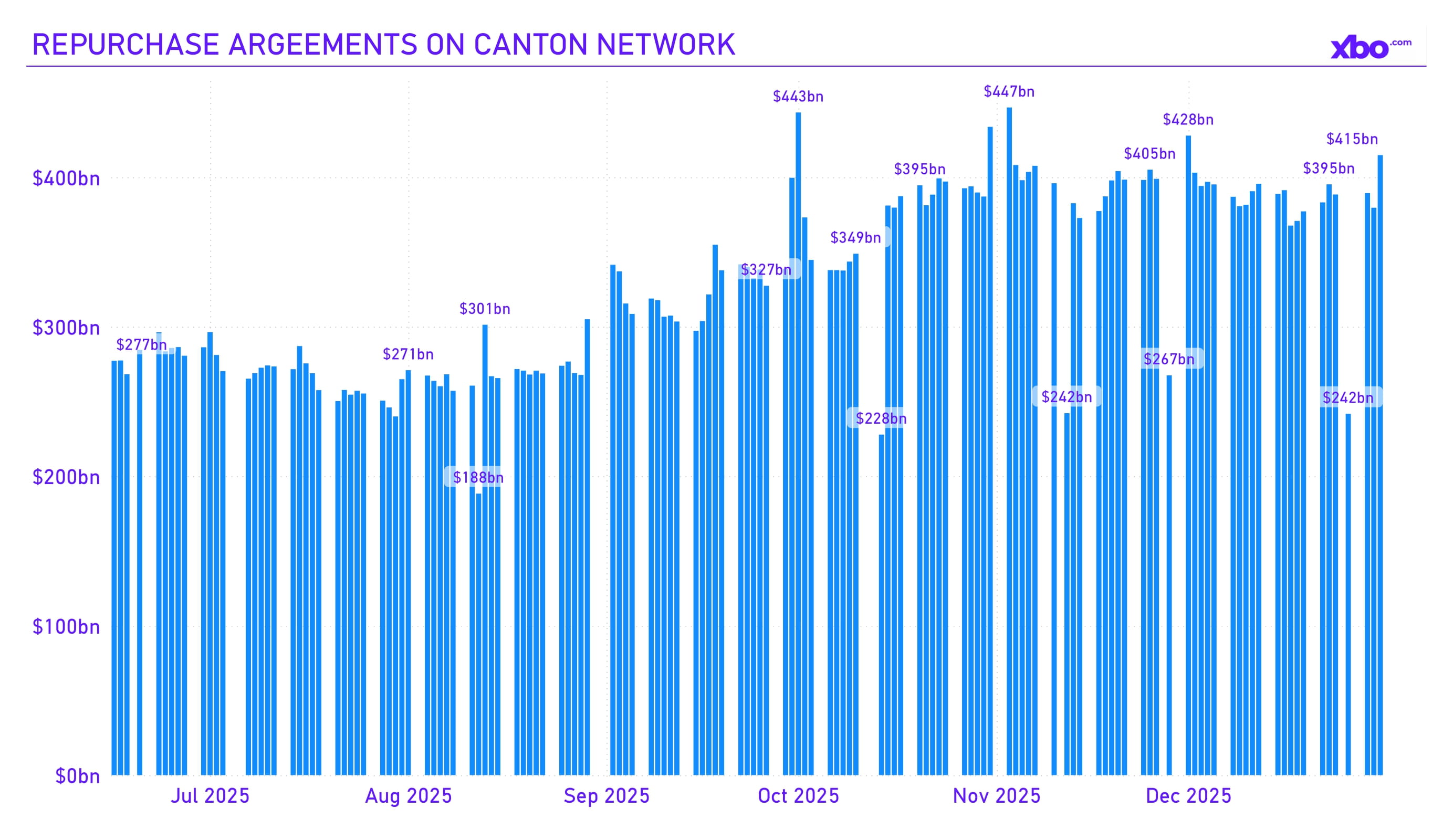
Source: app.rwa.xyz
The tokenization of repurchase agreements was another notable development in this regard. Thus, in the fourth quarter, the Canton Network advanced the tokenization of repo deals with US Treasuries. Since then, the platform has processed real on-chain repos with daily volumes exceeding $280 billion, as per Broadridge. DTCC officially joined the project: the launch of an MVP for tokenization of assets held in DTC custody is planned for the first half of 2026, with subsequent expansion. Tokenized repos provide atomic settlement 24/7, including weekends, reducing risks and increasing liquidity. This development represents one of the largest institutional steps toward RWA on blockchain.
Altcoins and DeFi in Q4 2025 strengthened economic interconnections, with RWA and tokenized assets linking crypto to traditional finance. In the US, this supported fiscal stability by increasing demand for Treasuries as reserves, aiding the $38.4 trillion national debt, while introducing systemic risks similar to bank runs in the event of a DeFi liquidity crisis.
Q4 2025 Summary
In the fourth quarter of 2025, the crypto market underwent a significant correction driven by US macroeconomic challenges, including inflationary pressure, government debt rising to $38.4 trillion, and uncertainty in Fed monetary policy. Bitcoin and Ethereum demonstrated a relatively weak performance, falling 20–23%, while altcoins lagged even further, except for privacy and AI sectors.
Meanwhile, institutionalization progressed: inflows into crypto ETFs exceeded $33.5 billion for the year, corporate BTC purchases increased by about 195,000 coins, and stablecoin capitalization reached $297 billion, confirming their role in global payments and asset tokenization. DeFi and RWA sectors showed mixed dynamics, with TVL growth in native tokens and tokenized repo deal volumes exceeding $280 billion daily, enhancing crypto integration with traditional finance.
Despite short-term volatility and systemic shock risks, fundamental improvements – from Ethereum upgrades to regulatory clarity – set the stage for recovery in 2026. Ethereum and infrastructure projects are expected to show stronger performance, with crypto positioned as a hedge against inflation, provided there is a balance between innovation and regulation.









